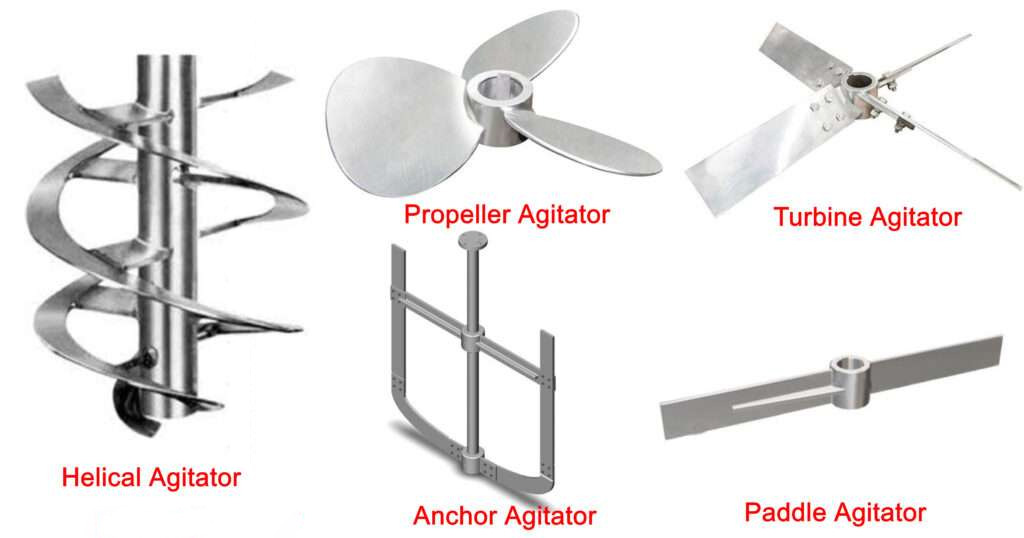

1. Unsaturated polyester resin (UPR)
Recommended blades: Anchor type + paddle type composite
Reason: UPR viscosity gradually increases during the reaction process, and it is easy to hang on the wall and agglomerate. The anchor type can scrape the wall to prevent dead corners, and the paddle type promotes flow and uniform heating. The mixing reaction is mild, and the heat conduction efficiency is required to be high.
2. Epoxy resin
Recommended bladdes: Turbine type / propulsion type
Reason: Most epoxy resins have medium viscosity during synthesis, and require good shear dispersion and uniform reaction environment. The turbine type provides strong shear force, which helps to speed up the reaction speed and improve the stability of epoxy value.
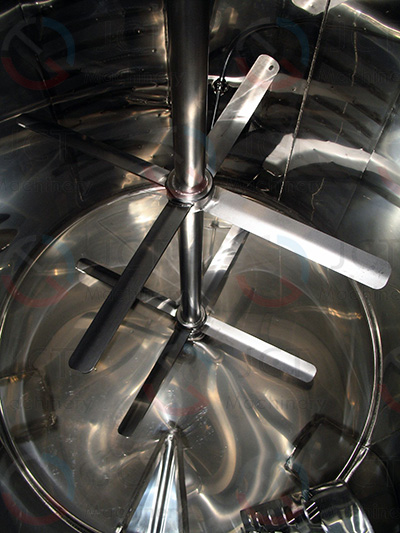

3. Alkyd resin
Recommended bladdes: Anchor type + paddle type
Reason: The viscosity changes from low to high, and the reaction requires long-term hear preservation. The material is prone to local heating and coking. The anchor type ensures wall scraping and paddle type maintains internal convection. Ensure uniform overall temperature distribution to prevent resin coking.
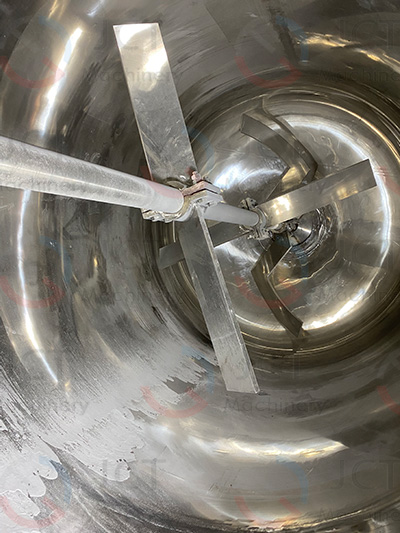

4. Polyurethane resin
Recommended bladdes: Screw ribbon / double helix + anchor type
Reason: PU is mostly a high viscosity system, especially in the prepolymerization stage, the stirring resistance is large, and the material needs to be forced to turn. The screw ribbon can efficiently promote axial and radial flow, and the anchor type assists in scraping the wall.
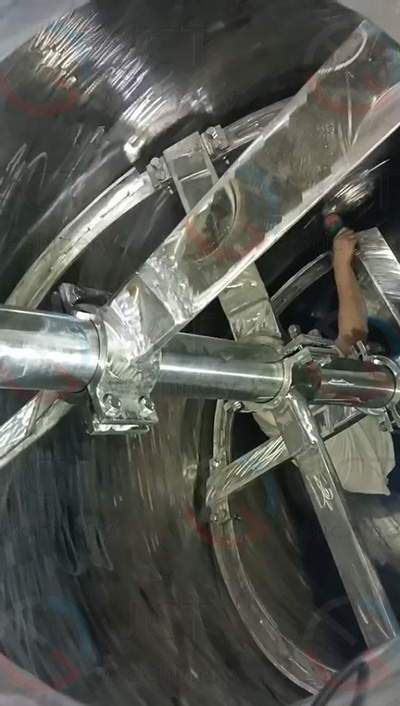

5. Phenolic resin
Recommended bladdes: Anchor / turbine
Reason: The viscosity is medium to high, and the reaction heat is strong, which is easy to produce local high temperature. The paddle is required to quickly take away the heat and keep the stirring uniform.
6. Hot melt glue
Recommended bladdes: Screw ribbon type
Reason: Typical high-viscosity system, high temperature control requirements, strong kneading and mixing, suitable for molding materials, and high efficiency of screw ribbon pushing.

 Home
Home JCT
JCT  May 29,2025
May 29,2025 
 5 Reactors Under Construction
5 Reactors Under Construction 







