What is phenolic resin?
Phenolic resin, also known as bakelite or phenolic plastic, is a high molecular weight polymer produced by the condensation reaction of phenolic compounds (such as phenol and cresol) and aldehydes (mainly formaldehyde) in the presence of acidic or alkaline catalysts.
Classification of Phenolic Resin
- Thermosettign phenolic resin (PF): This resin no longer melts after curing and is commonly used in molding compounds and laminates.
- Soluble phenolic resin (Resol): It is soluble and meltable, making it suitable for coatings and adhesives.
- Modified phenolic resin: It can be blended with urea, epoxy, rubber and other materials to improve toughness and impact resistance.
Applications of Phenolic Resin
- Adhesive: Used in plywood, wood-based panels, friction plates and high-temperature bonding.
- Molding compound: Used in manufacturing electrical switches, telephone housings and automotive parts.
- Coating and impregnant: Used in high-temperature resistant coaitngs and anti-corrosion coatings.
- Foundry industry: Used as a binder for phenolic resin sand cores.
- Aerospave and military industries: Used as a matrix for high-temperature resistant composite materials.
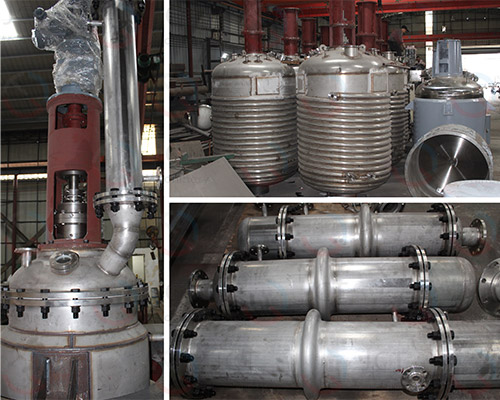

Phenolic Resin Production Line Equipment
1. Reactor
Material: Commonly stainless steel, with carbon steel lining available for some processes.
Heating method: Thermal oil, electric heating or steam heating.
Configuration: Equipped with agitator (anchor/paddle/propeller), condenser reflux device and temperature/pressure/vacuum control systems.
Purpose: Completes the polycondensation reaction between phenols and formaldehyde to produce different types of phenolic resisn.
2. Condenser
Used for condensing and recovering water vapor, formaldehyde vapor and by-products during the reaction, minizing material loss and energy conservation.
3. Water separator (Dehydrator)
Phenolic resin production requries strict control of the moisture content of the condensation reaction. A water separator effectively removes the generated water to increase the resin molecular weight.
4. Vacuum system
Used for subsequent cooling and dehydration, helping to improve resin yield and purity.
5. Storage tank and transportation system
Includes phenol storage tanks, formaldehyde storage tanks and finished resin storage tanks, equipped with explosion-proof pumps and safety valves.
6. Cooling and discharge system
After the reaction is complete, rapid cooling is required to maintain the resin's properties. Discharge can be by pump or bottom valve.
7. Crushing, drying and granulation equipment (for solid phenolic resin)
Spray dryer/vacuum dryer/granulator
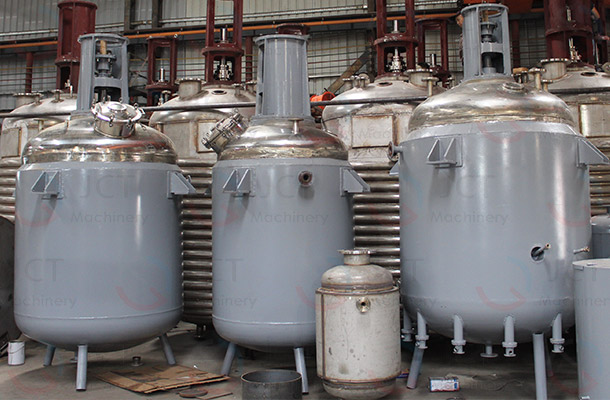

Features of Phenolic Resin Production Line
- Anti-corrosion and explosion-proof design (formaldehyde is highly corrosive and toxic, and phenol is also a hazardous substance, so the equipment must be corrosion-resistant and equipped with explosion-proof motors).
- Automated control (temperature, pH, pressure, vacuum and reaction time are automatically controlled to ensure batch stability).
- Environmental protection devices (exhaust gas absorption tower and condensate recovery system reduce formaldehyde emissions).
- Flexibility (the production of different phenolic resin types can be switched as needed: thermosetting, thermoplastic and modified phenolic resins).

 Home
Home JCT
JCT  Aug 14,2025
Aug 14,2025 
 Win The Market With Acrylic Resin And Acrylic Emulsion Production Line Turnkey Projects
Win The Market With Acrylic Resin And Acrylic Emulsion Production Line Turnkey Projects 







